What triggers electrical overloads, and what signs should you look out for? Prevent the silent threat lurking in overloaded circuits with this focused guide. Discover how to audit your Sydney home’s electrical demand, steer clear of circuit over capacity, and maintain a safe energy use balance.
Key Takeaways
- When a circuit draws more power than it can safely handle, an electrical overload can cause damage like fires or electrical faults. To prevent this, it’s important not to exceed 80% of a circuit breaker’s maximum capacity.
- Signs of an overloaded circuit include flickering or dimming lights, warm outlets, buzzing noises from outlets, and frequent tripping of circuit breakers. To prevent overloads, balance the load on circuits and upgrade outdated systems.
- Use energy-efficient devices, unplug appliances when not in use, and call a professional electrician for persistent issues or to perform system upgrades to prevent and handle electrical overloads.
Understanding Electrical Overloads and Their Impact
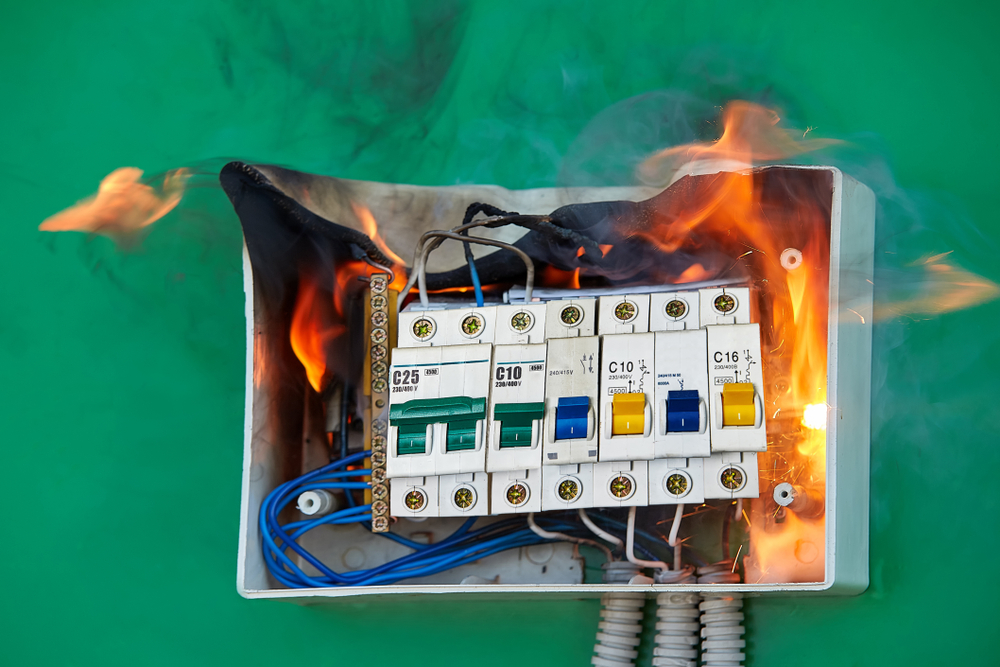
An electrical overload is a scenario where your electrical circuit is overloaded, drawing more electricity than it can safely handle. It’s like trying to fit ten people in a five-seater car – something will go wrong. The overload often occurs when multiple high-wattage appliances are used simultaneously or when many devices are connected to the same circuit using double adapters and extension cords. It’s a common issue in our gadget-filled modern homes.
The risks associated with electrical overloads are not to be underestimated. Overloading can lead to:
- overheating of wires, which can increase resistance and potentially cause fires
- damage to the insulation around the wires, increasing the risk of electric shock
- electrical fires that endanger both property and occupants
So, how can you avoid this predicament? Understanding the basics of electrical overload and recognizing the signs of an overloaded circuit.
The Basics of Electrical Overload
An electrical overload, also known as a circuit overload or electrical circuit overload, happens when a circuit draws more power than it can handle. Like a marathon runner pushing past their endurance limit, the circuit eventually trips, causing a power disruption. This overload can be caused by plugging in too many appliances on the same circuit or using extension cords to add more outlets. Electrical circuit overloads can lead to severe consequences if not addressed promptly, making it crucial to properly understand and maintain electrical circuits.
It’s recommended not to exceed 80% of a circuit breaker’s maximum amp value to prevent overloads. That’s like not filling your car’s boot to its brim to avoid overloading the suspension. The total load on each circuit is determined by summing the wattage of all devices on that circuit. Exceeding the circuit’s safe capacity can cause damage to equipment and fire hazards and reduce the lifespan of electrical components. It’s like overloading a washing machine – it might not break down immediately, but it will indeed reduce its lifespan.
Recognising the Signs of an Overloaded Circuit
Just like recognizing the signs of a common cold, identifying the signs of an overloaded circuit can be a lifesaver. Common signs include:
- Lights that flicker or dim, indicating voltage drops in an overloaded circuit
- Tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses
- Buzzing or crackling sounds coming from outlets or switches
- Burning smells or scorched marks around outlets or switches
- Appliances or electronics that don’t work correctly or keep shutting off
Imagine you’re at a concert, and the lights begin to flicker – it might be time to start looking for the exit!
Some signs of electrical overload include:
- Warm outlets or switches
- Tripped circuit breaker
- Discoloration on power points or light switches
- Burning odor from overheating components
- Variability in how well appliances function
These signs are like your body telling you something is wrong – paying attention and taking action is crucial.
Navigating Your Home’s Electrical System
Now that we understand what electrical overloads are and how to spot them let’s take a deep dive into the heart of your home – your electrical system. At its core is the main panel. Think of it as the control centre of your home’s electrical system, where the entire circuit and power distribution are managed. It’s like an orchestra conductor, ensuring every instrument (or in this case, appliance) performs in harmony.
Within this central panel, you’ll find circuit breakers. These are your home’s superheroes, stepping in to limit power to a safe level for the wiring system. They ensure power distribution is carried out according to the circuit’s safe capacity, preventing electrical overloads. Understanding the capabilities of your wiring system is crucial in ensuring it can safely handle your home’s power consumption. But how do circuit breakers work, and how can we assess our circuit’s capacity? Let’s find out.
Circuit Breakers: Your First Line of Defense
Circuit breakers act as the protective shield for your electrical system, preventing potential damage and hazards. They work by interrupting the flow of electricity when a fault is detected, ensuring the safety of your home or facility. They protect against electrical overloads by detecting excessive current flow and interrupting power to prevent overheating. When too many devices are connected to a circuit, leading to an excessive draw of energy, circuit breakers step in, shutting off power to prevent overheating and potential fires. They’re designed for a specific capacity, matching the load the wires can safely carry and tripping to cut power when demand exceeds this capacity.
And here’s the best part: unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset and reused multiple times after tripping, making them a practical and cost-effective investment for home safety. So, the next time your circuit breaker trips, remember it’s just doing its job – protecting you and your home.
Assessing Your Circuit Capacity
Assessing your circuit capacity is like judging whether a bridge can handle the weight of the vehicles passing over it. The maximum load an electrical circuit can handle safely is determined by factors such as the gauge of the wire and the circuit breaker’s rating. The electrical panel’s capacity also plays a significant role in determining the maximum load..
To determine if a circuit will overload, you can use the formula Watts = Amps x Volts to calculate the electric load capacity, which helps you understand how much power it can handle. This is similar to calculating how much weight a bridge can handle before it collapses.
The total daily electrical load is determined by adding all appliances’ daily energy consumption values, ensuring the electrical system can handle peak loads during simultaneous operation.
Not exceeding 80 per cent of the rated load on each circuit is recommended for safety. For example, a 15-amp circuit should have a maximum load of 1,440 watts and a 20-amp circuit should be limited to 1,920 watts.
Proactive Measures to Prevent Circuit Overloads
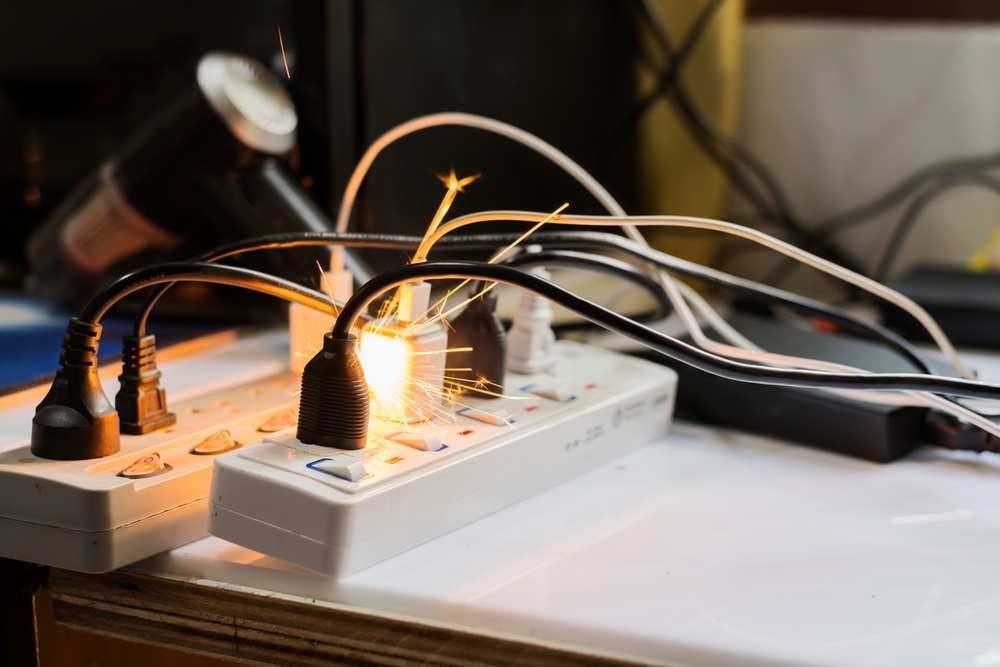

With a firm understanding of electrical overloads and a grip on navigating your home’s electrical system, let’s discuss proactive measures to prevent circuit overloads. We all know prevention is better than cure; the same principle applies to your electrical system. To avoid circuit overloads, it’s essential to stay aware of the amperage rating of breakers or fuses, keep the load under 80 per cent of that rating, and monitor the number of appliances connected.
Incorporating energy-efficient devices into your home can also mitigate the risk of overload as they consume less power. It’s like walking or cycling instead of driving – it’s better for the environment and your health (or, in this case, the health of your electrical system). But how can we use appliances smartly, and what should we do about outdated electrical components? Let’s explore further.
Balancing Power Consumption Across Circuits
When preventing circuit overloads, balancing power consumption across circuits is key. It’s like balancing the load in a boat to prevent it from tipping over. Regular tripping of a circuit breaker suggests excessive power demand from the circuit, indicating a need to redistribute appliances across different circuits or upgrade the electrical system.
To manage appliance usage effectively and avoid overloads, follow these steps:
- Check the wattage on the tags of each appliance.
- Calculate their estimated daily usage.
- It’s like planning your meals to ensure a balanced diet.
- This will ensure your home’s electrical system stays healthy and overload-free.
Upgrading Outdated Electrical Components
Just like you’d replace an old, worn-out car tyre, upgrading outdated electrical components to improve safety and accommodate modern appliances is crucial. Modernizing electrical wiring in older homes can provide more power to support the increased energy demands of contemporary appliances and electronics, reducing the risk of overloading. Plus, upgrading old wiring systems can significantly improve the safety of your home, preventing power surges and reducing the risk of fires.
Consider implementing energy-efficient solutions like LED lighting to reduce overall energy consumption during the upgrade process. It’s like upgrading your old gas-guzzling car for a more fuel-efficient model – it’s better for your pocket and the environment.
Smart Appliance Usage to Avoid Overloads
As we move into the digital age, our homes are increasingly filled with appliances and gadgets. This makes it even more critical to use these appliances smartly to avoid overloads. Having dedicated circuits for high-power-consuming appliances like air conditioners ensures they do not cause overloads when used simultaneously with other common appliances such as washing machines, refrigerators, or dishwashers. It’s like assigning a separate lane on the highway for trucks to prevent traffic jams.
Additionally, using energy-saving appliances can significantly lower the electrical load on circuits, which not only helps prevent overloading but can also lead to savings on power bills. It’s like replacing your old appliances with energy-efficient ones to save on electricity and reduce the risk of overloading your circuits.
But how can we prioritize appliance use and minimize power draw? Let’s find out.
Prioritising Appliance Use
Prioritizing appliance use is like planning your day – you must decide what tasks are most important and do them first. In the case of appliances, using them sequentially instead of simultaneously helps manage energy loads and prevent circuit overloads.
For example, you might want to:
- Run your dishwasher at night when other high-power devices are not in use.
- Use your washing machine during off-peak hours to avoid straining the electrical system.
- Wait to use your oven until you’ve finished using other high-power appliances.
By prioritising your appliance use, you can use energy efficiently and avoid potential electrical issues.
Also, consider the duty cycle of your appliances. Continuous loads operate for three or more hours at full capacity, while non-continuous loads operate for under three hours. Prioritise high-power consumption devices by running them at different times, especially those classified as continuous loads, to minimize the risk of overloading circuits.
It’s like scheduling your day to ensure you don’t burn out by doing too many strenuous tasks simultaneously.
Unplugging Devices Not in Use
Did you know plugged devices can still consume energy even when turned off? This unnecessary power draw is known as standby power. It’s like leaving the tap running when you’re not using it – a waste of resources.
Adopt the habit of:
- Unplugging entertainment systems and gaming consoles when not in use to minimize continuous power draw
- Using power strips with on/off switches to easily disconnect multiple devices at once and reduce the risk of overloading a circuit
- Reducing the chance of overloading by unplugging unused appliances to prevent power surges from exceeding circuit load capacity
It’s a simple habit that can greatly impact your home’s electrical health.
When to Call a Professional Electrician
While understanding your home’s electrical system and taking preventative measures is crucial, sometimes calling in the experts is best. If you’re dealing with:
- persistent circuit breaker trips
- flickering lights
- outlets that are hot to the touch
- frequent power outages
- outdated wiring
- your home’s electrical needs have outgrown the existing setup
It’s time to consult a professional electrician in Sydney. Consider it like calling a doctor when home remedies aren’t enough to treat your symptoms.
A professional electrician should be consulted to resolve electrical overloading circuits or perform necessary upgrades. If circuit breakers are repeatedly tripping or if heavy use of extension cords indicates insufficient outlets for your home’s needs, it’s time to call a professional electrician. It’s important to remember that working with electricity carries significant safety risks that require expertise and proper equipment to manage, similar to performing a complex medical procedure that requires a trained professional.

Dealing with Persistent Circuit Breaker Trips
Persistent circuit breaker trips are like a persistent cough – a sign that something’s not right and you need professional help. Homeowners should not attempt to fix electrical faults themselves and, instead, seek a qualified electrician’s assistance when experiencing circuit breaker problems.
Electricity is not something to mess with. If you’re unsure what you’re doing, it’s always best to call the professionals. Electrical service companies can provide residential and commercial electrical services to address persistent circuit breaker tripping issues.
So, when in doubt, call a professional!
Enhancements and Repairs by Experts
Regular electrical inspections by a professional can prevent potential hazards by identifying issues like outdated wiring or overloaded circuits. It’s like getting your car serviced regularly to ensure it’s running smoothly and catching any potential problems early.
Consulting with a professional electrical contractor is critical for expert maintenance advice, installation, and keeping the electrical system within safety compliance. So, if you’re unsure about anything, don’t hesitate to call in the experts. After all, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding, preventing, and managing electrical overloads is crucial for the safety and efficiency of your home. Overloads occur when the power demand exceeds circuit capacity, leading to potential safety risks such as fires and damaged electronics.
By knowing how to navigate your home’s electrical system, taking proactive measures to prevent overloads, using smart appliances, and knowing when to call a professional electrician, you can ensure your home is safe from electrical overloads. Remember, prevention is better than cure; the same goes for your home’s electrical health.
Mr Sparky is one of Sydney’s leading electricians, providing services locally in the Inner West, Marrickville, and across Sydney. If you need local help fast, look no further; we’ve got tons of 5-star reviews from happy customers, so rest assured you’re in safe and trusting hands for all your electrical needs.
Stay safe!
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if electricity is overloaded?
If electricity is overloaded, it can cause a circuit breaker to shut off temporarily or even lead to a fire due to overheating wires. Stay safe and be mindful of your power usage.
What are overloads often caused by?
Overloads are often caused by overuse of extension cords and multiple plug adapters on the same circuit, which place too much current demand on the circuit. Using too many high-power appliances simultaneously, such as blow dryers and curling irons, can also lead to overload.
What are three warning signs of an overloaded electrical circuit?
If you notice dimming lights when you turn on appliances, buzzing outlets or switches, or warm outlets or switch covers, these could be warning signs of an overloaded electrical circuit. It’s important to address these signs to prevent potential hazards.
What are the dangers of electrical overload?
Electrical overload can lead to power disruptions, equipment damage, fire hazards, and shortened lifespans for electrical components. Tripping of circuit breakers or bursting fuses acts as a safety measure to prevent further damage and potential dangers. Be mindful of electrical overload.
How do you fix electrical overload?
You can start by moving some appliances to a different circuit to fix electrical overload. If that doesn’t work, contacting a certified electrician for help is best.
Other Relevant Articles
Replacing Circuit Breaker: A 2024 Guide to Costs and Connections