Are you curious about the differences between single-phase and three-phase power? Perhaps you’re considering the “single phase vs 3 phase power” debate when upgrading your home’s electrical system or exploring solar power options. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of power supply is essential for making informed decisions that cater to your specific energy requirements. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of single-phase and three-phase power, their fundamental differences, and potential applications.
Key Takeaways
- Single-phase power is the most common type of electricity used in homes and small businesses, while three-phase systems are more efficient for industrial applications.
- Three-phase power has greater efficiency due to balanced distribution, higher power transfer capability and reduced current flow.
- Considerations when selecting an appropriate single or three-phase inverter include the size & scalability of the system as well as the existing grid supply.
Single Phase vs Three Phase Decision Checklist
- Power Requirements: Assess the total power requirement of your home. Three-phase power is typically necessary for homes with high power demands, such as large heating systems, air conditioning units, or heavy-duty appliances.
- Availability: Check the availability of three-phase power in your area. In some residential areas, only single-phase power may be available, or additional costs might be associated with installing three-phase power.
- Cost of Installation: Compare the costs of installing single-phase vs. three-phase power. Three-phase power installation can be more expensive due to the need for additional equipment and wiring.
- Efficiency: Understand that three-phase power is generally more efficient for running large motors and heavy electrical equipment. This efficiency can lead to lower energy bills in the long run if you have high power demands.
- Electrical Load Balance: Consider that three-phase power allows for a more balanced electrical load, which can benefit the longevity and efficiency of electrical appliances.
- Future Expansion: Think about future expansion plans. If you plan to add more heavy-duty appliances or electric vehicle charging stations, three-phase power might be a better choice.
- Resale Value: Evaluate how the choice between single-phase and three-phase power might affect the resale value of your home. Homes with three-phase power can be more attractive to specific buyers.
- Safety Considerations: Ensure that all safety protocols are followed during installation. A professional electrician should handle three-phase power installations.
- Local Regulations and Compliance: Check local building codes and regulations. Some areas have specific requirements or restrictions regarding the type of electrical system that can be installed in residential properties.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Consider the maintenance and servicing needs of both systems. While three-phase systems are generally more robust, they may require more specialized knowledge for servicing and repairs.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer to make the best decision based on these factors and your specific needs.
Unraveling the Basics of Single-Phase and 3-Phase Power
Electricity is fundamental in our daily lives, powering a wide range of items from our household appliances to industrial machinery. Two main types of electricity supply dominate the electrical landscape: single-phase and three-phase power. Although these terms may sound technical, they describe how electricity is generated, transmitted, and consumed. Understanding the basics of single-phase and three-phase power is the first step in grasping their differences and respective applications.
Knowing the features of single-phase and three-phase power is beneficial for homeowners planning to upgrade their electrical systems or business owners assessing power options. The choice between the two depends on various factors, such as the size of the electrical load, the type of appliances being used, and the specific electrical installation requirements.
Defining Single-Phase Power Supply
Single-phase power supply is the most common type of electricity used in homes and small businesses. This type of power supply consists of two wires: a phase wire and a neutral wire. Single-phase power is characterized by a single alternating current (AC) waveform, typically 230V at a frequency of 50 Hertz. The single-phase connection is established through these two wires.
A single-phase power supply’s simplicity and broad availability make it perfect for domestic and minor power needs. However, it does have some limitations. For instance, single-phase power supplies cannot provide power to large electric motors and struggle to deliver continuous power to the load. This is why understanding the capabilities of a single-phase supply is essential for making informed decisions about your power needs.
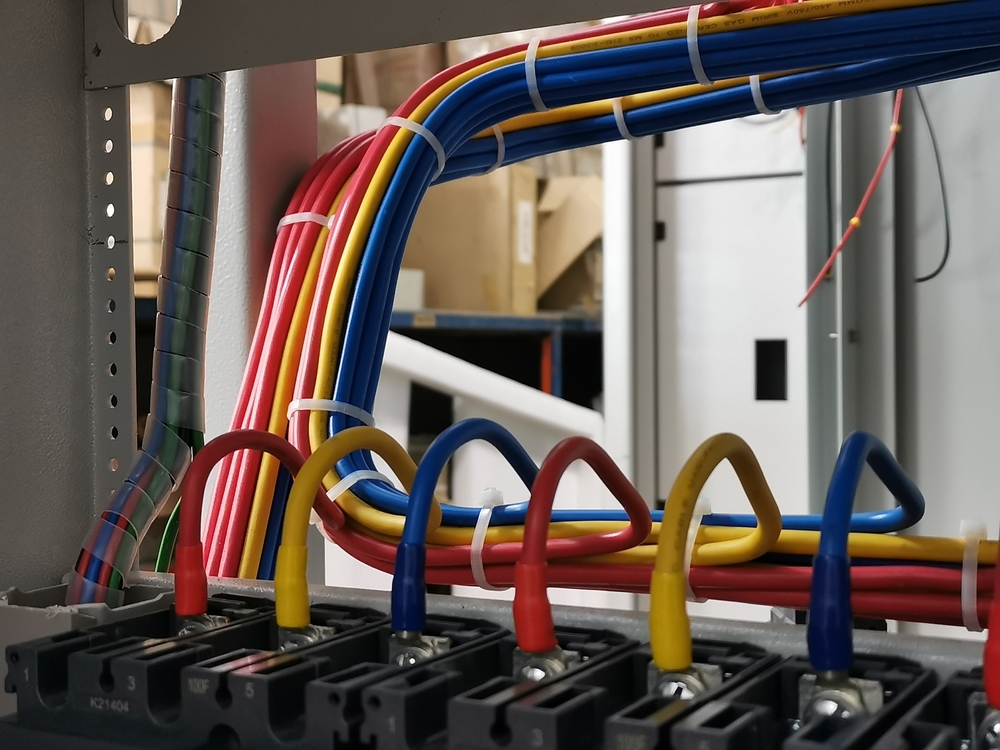

Understanding Three-Phase Power Supply
On the other hand, a three-phase power supply is designed for larger loads and industrial applications. It involves three or four wires, with three-phase wires delivering power 120° out of phase, providing a more efficient and reliable power supply. This increased efficiency and power transfer capability make it a popular choice for commercial and industrial settings, where it is used for:
- Large machinery and equipment
- Motors and generators
- Industrial heating and cooling systems
- Manufacturing processes
Overall, phase supply is essential for meeting the high power demands of industrial applications, especially for three-phase power supply, also known as three-phase supply.
The main advantage of a three-phase power supply is its heightened efficiency and better power transfer ability compared to single-phase power. It is also more suitable for heavy machinery, offering consistent power delivery. However, a three-phase power supply requires more complex wiring and may incur higher installation costs.