What is a Circuit Breaker?
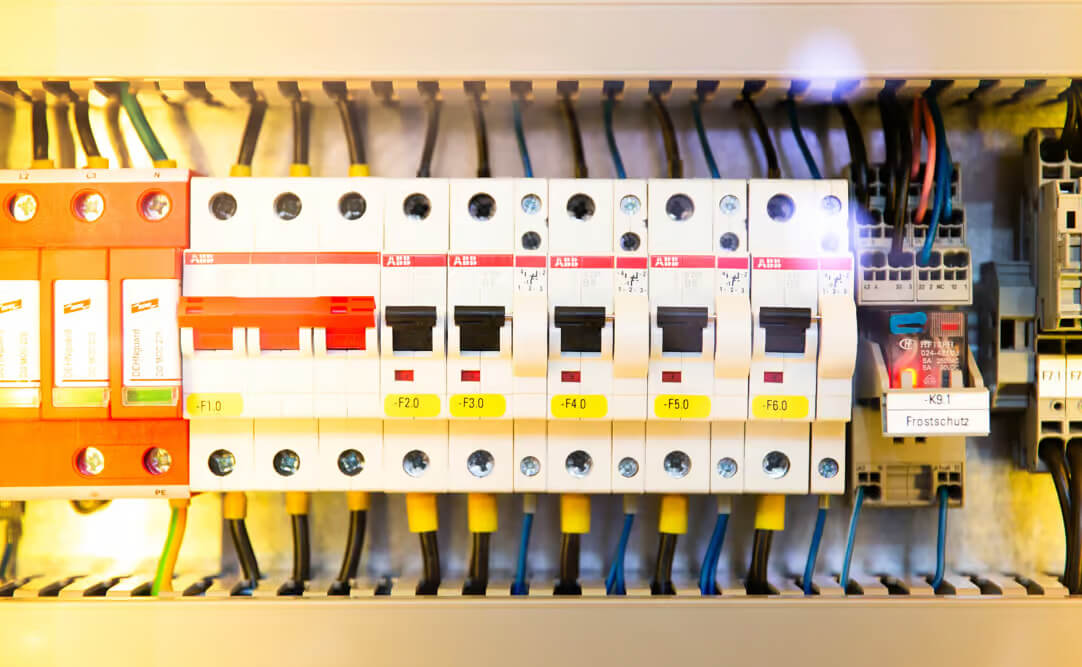
Circuit breakers play a vital role in electrical systems.
Their primary function is to detect and respond to electrical faults, such as overcurrents and short circuits.
Circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity when these faults occur, effectively protecting the electrical circuits and preventing damage to electrical equipment.
There are different types of circuit breakers, including thermal, magnetic, and combination, each with specific features and applications.
What is a Safety Switch (Residual Current Device)?
Safety switches, also known as residual current devices (RCDs), serve a different purpose than circuit breakers.
Their main function is to detect electrical leakage and ground faults, which can pose a significant risk of electric shock and electrocution.
Safety switches are designed to quickly interrupt the power supply when they detect such faults, minimising the risk of fatal accidents.
There are various types of safety switches available, including RCDs, RCCBs, and RCBOs, each suited for different electrical protection requirements.
Functions and Protection of Circuit Breakers and Safety Switches
Circuit breakers provide protection against overcurrents and short circuits. They are essential for preventing electrical fires and damage to electrical equipment. By interrupting the flow of electricity when faults occur, circuit breakers ensure the integrity and reliability of electrical circuits. It’s crucial to install correctly sized circuit breakers for each circuit to ensure effective protection.
On the other hand, safety switches focus primarily on protecting against electrical shock hazards. They detect electrical leakage and ground faults, which occur when electricity flows through unintended paths, such as a person’s body. By quickly interrupting the power supply upon detecting these faults, safety switches minimise the risk of electric shock and potential fatal accidents. Proper placement of safety switches near power outlets, particularly in wet areas, is crucial for comprehensive electrical protection.
Importance in Electrical Safety
Circuit breakers are crucial for safeguarding electrical systems and preventing damage. They ensure that electrical circuits are protected from excessive currents and short circuits, which can cause overheating and electrical hazards. By preventing electrical overloads, circuit breakers play a vital role in maintaining the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
Safety switches, on the other hand, are of utmost importance in minimising the risk of electric shock, which can be life-threatening. They provide an additional layer of protection by detecting electrical leakage and ground faults, protecting individuals from the hazards of electrical current flowing through unintended paths. Safety switches are not only crucial for personal safety but also essential for preventing electrical fires and property damage.
Key Differences Between Circuit Breakers and Safety Switches
One key difference between circuit breakers and safety switches lies in their operation and detection mechanisms. Circuit breakers detect excessive currents and short circuits, while safety switches focus on detecting electrical leakage and ground faults. These distinct mechanisms enable circuit breakers to protect against damage to electrical systems, while safety switches prioritize protection against electric shock hazards.
Another difference lies in their applications and placement. Circuit breakers are typically installed in the main electrical panel and provide protection for the entire electrical system. Safety switches, on the other hand, are strategically placed near power outlets, particularly in wet areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor areas. This placement ensures that safety switches can quickly interrupt the power supply in the event of a fault, reducing the risk of electric shock.